What is Micro Service?
Architecture style to build Autonomous, independently
deployable services collaborate together to form an application.
You must have worked on and may be created applications
without calling micro services.
How small it should be – depends
Why do we need micro service ?
Monolith – software typically all application is in a Single
Codebase.
Single
Codebase – exist in a source repository where all developers collaborate each
other.
Typically build artefact runs in a
Single
Process – build the artefact
Single
host - runs on a single host.
Single
Database – persist to
Consistent
Technology – dev env, single programming language, sdk used
Benefits of Monolith
Simplicity
One
codebase – easy to find
Deployment
– one application to replace
Nothing wrong. Then Why we need micro services? or You don’t
Micro services, Yet
Problem of scale
Many
developers , many users, many data, code base grow- difficulty in maintain (
growing complexity and accumulation of technical debt) , entangled modules (
wired here and there, although u put an effort and build a modularised app)
Deployment – single line of change need to deploy the whole
app
Risky
Usually
requires a significant downtime
But
some use modern level cloud services
Difficult to Scale – unless you make it stateless
Horizontal
scaling often not possible
More
possibility towards vertical scaling
Too
expensive , add more hardware(memory, hard disk , processor etc)
Whole
application must be scaled
Finally -
Wedded to Legacy technology
Have
to upgrade entire application to move to a newer frame work
Reduces
agility – ability introduce new practices, take advantage of innovation
Distributed monoliths
You can argue my app is not a monolith. It has few services,
just like CMP
SOA – service oriented architecture
System built as services, but
Uses a
single database
Tightly
coupled
Everything
must be deployed together (or few together)
New
features require, changes every where
This where you need to understand what micro services else
you will end up building something worse than monolith or distributed monolith
(SOA)
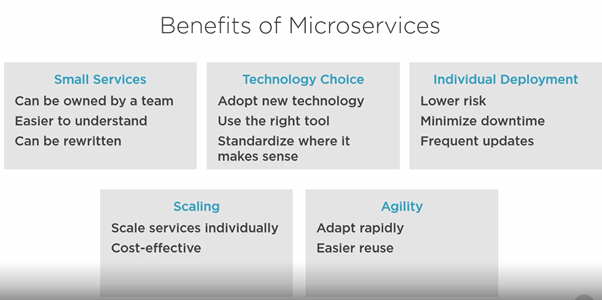
How are micro services better than Monoliths?
Small services
Can be owned by a team
Easier to understand
Size – small enough to be thrown
away and rewrite
Technology Choice
Adopt new
technologies - without upgrading whole
application as Monolith
Use the
right tool – for specific task
One
might use relational database where other document database
Object
oriented programming language , other functional programming language
Standardize
where it makes sense – but no hard rules, common agreement like in REST
Individual deployment – cause of loose coupling
Lower
risk – no need to upgrade, deploy entire system in one go
Minimize
down time – zero downtime
Frequent
updates
Scaling
Scale
services individually
Cost
effective – compared to monolith
Agility
Adapt
rapidly – for changing business requirements
Easier re
use
Downsides – New Challenges – Not a free lunch - whether micro services a good solution for
you
Challenges
Developer Productivity
How can we make it easy for developers to be productive
working on the system?
Do they have to download code for every single micro
service?, run individually, configured them to talk to each other, That can be
error prone and time consuming , way of easily working on a single micro
service and as well as testing in the context of whole application
Complex Interactions
Take car to avoid inefficient, chatty communications between
micro services
IF we brake application for dozens of micro services then
interactions may be complicated.
Deployment
You will need to automate the process – you will have lots
of micro services
Monitoring
We need to have a centralized place to check the logs and
monitor for problems – cause you cannot
go to each service and find logs
These are just a few
So lots of challenges – good news- you have lots of patterns
and technologies to help you to overcome these challenges
Micro services – Do not dictate on
What
technology
What type
of data base you use
What type
of communication – asynchronously or synchronously
What
authentication mechanism
Completely free to use your favourite| best programming
language, tools
Micro services Architecture(wrap up)
-
Comparisons with monoliths
-
Benefits
-
Challenges
--
Build a new app using Micro services architecture or to
migrate monolith to microservices
Need to make Important Architecture decisions upfront
You do not have start with a micro service, but possible to
evolve existing app step by step
Evolving towards micro services
-
Micro services are autonomous – which means own
its own data
-
Own their data
-
Independently deployable – clearly defined and
backward compatible public interfaces
-
Identifying micro service boundaries – very
tricky, breaking monolith, boundary to context
-
What if I have a monolith already?
-
Augment a monolith
o
Add new micro services
-
Decompose a monolith
o
Extract micro services
-
No need to start with a micro service
o
Hard to get the service boundaries at start
o
Benefits are not seen in small projects
o
Let the app grow a little and then segregate for
micro services
Micro service Own data
Avoid sharing a data store – data store per service
Limitations
-
Data base joins – in two different databases
-
Transactions – cannot update two tables in two
dbs,
o
Either use distributed transactions – very
complicated or design our application to work in a ENETUALLY CONSISTANT manner
-
Eventual Consistency
o
May have to wait a while for overall state of
the data to be fully consistent. What this means in practise, when a single
business process requires to update more than one data source, there will be a
small window of time when changes made in one data store, but not the other. So
you need to design your applications in a such a way that it handle this Temporary
Inconsistency.
o
Summary
Evolving towards Micro service
Micro service own their data
May consist of multiple processes
Should be independently deployable
Avoid breaking changes – changing APIs
Identify “Bounded Context”
for micro service boundaries
Getting boundaries right – critical factor
Micro Service Hosting
Options
-
Virtual Machines
VM per
service – can be little costly , cause there are so many
Few
services in one VM – but can be messy as each MicroService has its own requirements, frameworks, database,
performance etc.( you can imagine with running few monoliths one machine)
-
Operational challenges
-
Service Discovery
Platform as a Service
Automatic Scale out
DNS address
Load balancing
Security
Monitoring
Serverless – nano services
Containers package up applications
Portable – run any where
Easily run locally
Docker compose
Use cloud – Paas – then you need invest more, cause as micro
services grow – productivity of the developers drop
Creating New
MicroService
-
Source control
repository per micro service
o
Avoid tight coupling between services
-
Continuous Integration build
o
Run automated tests
Types of Tests
-
Unit Tests -fast to run, high code coverage
-
Service level test – Integration test, Test
single service in isolation, Mock collaborators, Invest for Framework creating
service level test
-
End to End Test – Production like env, Can be
fragile,
Micro Services templates
Standardize
Logging – all logs in a same format
Health Checks –
Configuration –
Authentication
Build scripts – use
containers, docker
Increase Productivity
Developers focus on implementation of Business logic rather
than plumbing infrastructure
Connected shared services – cloud services
Communicating between MicroServices
Asynchronous and Synchronous communication patterns
Calling MicroServices
Are there any rules, can any service can call each other
Web, Mobile etc allowed call MS directly.
There are no hard rules, but there are difficulties when
allowing free flow access and call
-
End up making Tangled dependencies
-
Making cascading failures – one MS fail, causes
to fail others as well
-
Poor performance – call to one MS ends up with
calling dozens of MS call call hops
-
Mispalce (service) boundaries
Better
-
Minimize call between MS – you can publish
through event BUS, subscribe to services via BUS
-
Promote Asynchronous call between MS
-
Front end app, Single page app, Mobile – without
coming directly use a pattern call API Gateway – will have several benifits
o
Authentication – API Gateway level, security can
handle from single point
o
Front end apps needs to know how to call
different MS
o
Decouple Front end apps with MS , backend APIs
o
Micro Services do not call each other, Instead create events
in Event Bus
Event Bus implemented in either RabbitMQ when we run locally
or Azure Service Bus when running cloud
Messages are subscribed by MS and handled Asynchronously.
So use different communication patterns, suitably as shown.
API gateway for Each level
Synchronise Communication
Eg: Retrieve information from DB, select query
This is an Asynchronous call – customers do not want to
wait.
HTTP
-
Industry Standard
-
Can take advantage
o
Standardize approach
o
Caching – standard error codes
o
Payloads -JSON {native format of javascript,
support by many, easy}, XML
o
-
Implement APIs as a set of resources (RESTful
APIS)
o
Eg: Catalog Item, Order {Information as
resources}
-
Use standard HTTP methods
o
GET to retrieve, PUT
-
Good use of HTTP status Codes
-
Media Type headers (Content Type)
Rest is a big Topic. This is just a little
Asynchronous Communication
When we cannot expect
user to wait until everything is finished.
Communication over HTTP
Send status code “Accepted” rather than “OK” – then user can
check the status later
Callback – MS itself reports back when task is complete.
Client can register for callback URL , on which they like to receive
notification
Via Messaging
With registering to even BUS, others subscribe (rather than
calling directly)
1.
Simply creates a message and sends to “Message
Broker” – which acts as Intermediator.
2.
Other MSs subscribe to those messages
Act as an Intermediator , decouples micro services
completely.
Advantage for scaling – eg:If unprocessed messages growing,
you can simply scale out that MS with multiple instances.
Many “ServerLess” platforms does this automatically.
With containers also possible with configuring cluster of
services| containers
Message Types
-
Commands
-
Events
Command is an request to performed on particular action eg:
send a email
Events – something has happened, In Past Tense, several
actions might need to occur as result of that event eg: OrderPlaced ( charging
credit card, sending confirmation mail, checking on stock levels..)
RabbitMQ, Azure Service BUS
https://www.enterpriseintegrationpatterns.com/
Resilient Communication Patterns
We cannot expect service to be run 100% without error and
failure
Implement retry with backoff
First
attempt fail, wait little while – If second fail wait for more … back off
IF too
many attempts made – their can be denial of service attacks
Circuit breaker
Sit
between client and server
Passes
call through (circuit breaker is “closed”)
If enough
errors are detected, blocks further calls (circuit breaker is open)
After
time out – allows some calls to through, to see the problem has been resolved.
If OK – circuit close else open
Simple ,
but powerful – many have implemented – just use
Caching
Fallback to cache data, if service is unavailable
Messaging resilience ( Message Broker)
Inherent support for resilience
Idempotent
If
calling twice with same message will have same effect as call in once.
Eg: In e commerce sample app – we should have good check to
make sure for a order process multiple times – make sure ship once, charge once
for credit card
3.
You receive a message and partly processed and
something happens. As a result you receive it again.
Service Discovery
To MS to communicate
with each other – each should have an address
How to find and keep track
Service registry
When you need to communicate to MS, ask service registry –
where is that MS
Service Registry – typically distributed among all the
machines in the cluster. Which makes easy to contact service registry.
Service Discovery – Alternatives
DNS
If you using cloud – you automatically get DNS and plus load
balancing
If use Container such as Kubernetes
Built in
DNS – no need to know the IP address of each container , just need to know the
name of the service you need to call MS. It willtake care of routing traffic to
container you are running the service. Load balancing, if necessary.
So to handle challenges are much more easier – if you host
MS in modern platform
Securing Micro Services
You may use HTTPS – (TLS – Transport Layer with certificates
issues by trusted party), but it does not mean secure. You need to Authenticate
the user.
Authentication Option
-
Basic Authentication – User name and pass
Problem is every MS need to securely store passwords – need
best practises, better hashing etc
-
API key – (key per client , key management)
-
Client certificate (public key cryptography-
prove caller identity, but quite difficult to keep install and manage)
Is there a better way, one of the most promising approaches
– Identity server
Authorization server – takes care of the complexity of
authentication and authorization
1.
Client Authenticate with identity server by
sending credentials
2.
Identity server returns an access token (which
got limited life time)
3.
Access token in authorization header – to MS
(these are signed by public key cruptography helping the to verify )
4.
Verify Access token with Identity server
Here One service has the job of
Authentication
users and Managing their credentials securely.
Cause IS
implemented using Industry standard (OAuth 2.0 & OpenID connect) you don’t
have to write. You can make use of a third party solution. Writing IS is a lot
of work.




































No comments:
Post a Comment